DevOps Lesson
import socket
# Change the following host and see what IP it prints!
host = "google.com"
ip = socket.gethostbyname(host)
print(ip)
with socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) as s:
s.connect((ip, 80))
print("Successfully connected!")
with socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM) as s:
s.connect((ip, 80))
# Send a GET request to "/"
s.sendall(b"GET / HTTP/1.1\r\n\r\n")
# Recieve & print 2048 bytes of data
data = s.recv(2048)
print(data.decode())
import requests
# Change the URL to whatever you'd like
response = requests.get("https://youtube.com")
print("Status code:", response.status_code)
print("Headers:", response.headers)
print("Response text:", response.text[:100])
# Add a line to print the "Content-Type" header of the response
# Try an image URL!
aws = "3.130.255.192"
response = requests.get("http://" + aws)
print(response.text)
Configuration
server {
// Listen on virtual "port 80"
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name 3.130.255.192;
location / {
// Inform server about original client
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
// Forward all requests transparently to the server running on our computer
proxy_pass http://localhost:9099;
}
}
Load Balancing
upstream example.com {
server server1.example.com;
server server1.example.com;
}
HTTP Headers
server {
add_header X-Cool-Header "I love APCSP!";
location /pages {
add_header X-Cooler-Header "This is my secret header!";
}
}
Check In
- Research 1 HTTP header and describe, in detail, its purpose.
- One HTTP header is the "User-Agent" header, which provides information about the client (typically a web browser) making the request to the server.
- Write a line in a sample NGINX configuration that will add that specific header to the
/informationlocation ``` location /information { add_header User-Agent "Custom User Agent"; } - Explain the purpose of the load balancing performed by NGINX
- The purpose of load balancing performed by NGINX is to distribute incoming network traffic across multiple servers to improve reliability, scalability, and performance.
- Modify the following code block to obtain the value of the secret header on
/productsof the AWS site- Imported request and changed it so the varible was in the print stament
import requests
aws = "3.130.255.192"
response = requests.get("http://" + aws+ "/products")
print("The secret header is:", response)
Hacks
- Complete the above check-in questions and change the hosts (0.1)
- [x]
- Complete the above code-segment to retrieve the secret header (0.1)
- The secret header is: <Response [200]>
- The page: Hello, we sell: - iPhones - iPads - Mortensen keychains
Bonus (0.05)
Create a diagram showing the layers of abstraction that allow us to use HTTP (IP, TCP, etc.)
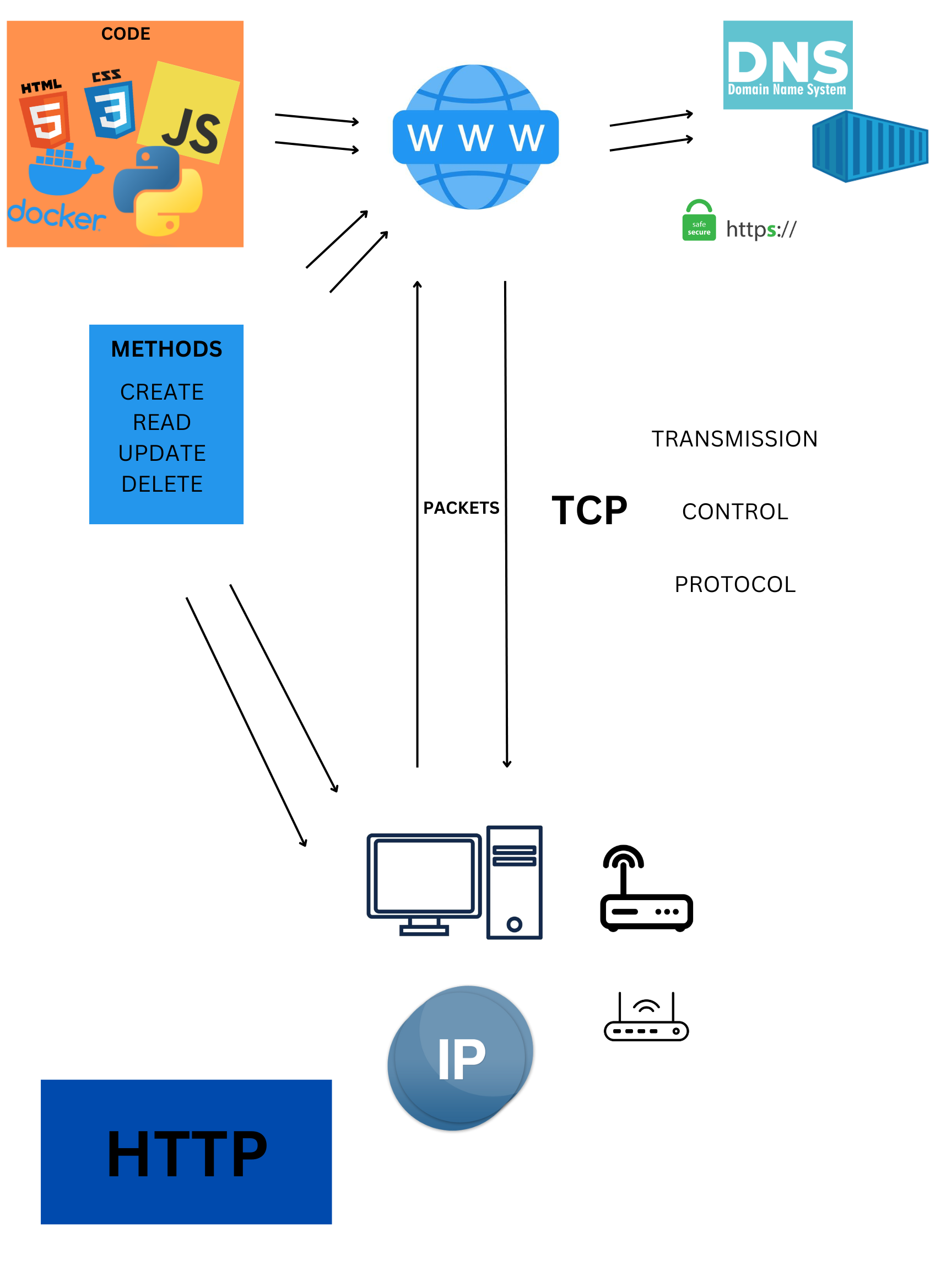
CORS Hacks
- Explain what CORS is and what it stands for
- CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) is a web security mechanism that allows web browsers to make requests to a different origin/domain than the one the website is hosted on.
- Describe how you would be able to implement CORS into your own websites
- To implement CORS in your website, you need to include appropriate CORS headers in the server's response, such as Access-Control-Allow-Origin, Access-Control-Allow-Methods, and Access-Control-Allow-Headers, which specify the allowed origins, methods, and headers for cross-origin requests.
- Describe why you would want to implement CORS into your own websites
- Implementing CORS in your websites is important to control which external domains can access your resources, enhancing security by preventing unauthorized cross-origin requests.
- How could use CORS to benefit yourself in the future?
- Using CORS in the future can benefit you by enabling you to build and integrate web applications that need to communicate with different domains, allowing you to create more dynamic and interactive websites with secure cross-origin data sharing.
Total: 0.2 points
KASM Hacks
- What is the purpose of "sudo" when running commands in terminal?
- The purpose of "sudo" (short for "superuser do") when running commands in the terminal is to execute the command with administrative privileges, typically as the root user. It allows users to perform actions that require elevated permissions, such as modifying system files or installing software.
- What are some commands which allow us to look at how the storage of a machine is set up as?
- Some commands that allow us to examine the storage setup of a machine include:
- "df" command: It displays information about disk space usage, including the available space, used space, and file system types.
- "du" command: It estimates file and directory space usage, providing a summary of the sizes of individual files or directories.
- "lsblk" command: It lists information about block devices, including disks and their partitions.
- What do you think are some alternatives to running "curl -O" to get the zip file for KASM?
- Alternatives to using "curl -O" to retrieve the zip file for KASM could include:
- Using a web browser to download the zip file manually from the KASM website.
- Using a download manager or wget command to retrieve the file.
- Using a version control system like Git to clone the KASM repository directly.
- What kind of commands do you think the "install.sh" command has and why is it necessary to call it?
- The "install.sh" command likely contains a series of instructions and commands that automate the installation process for KASM. It may include steps such as checking dependencies, configuring settings, copying files to the appropriate locations, and starting necessary services. Calling the "install.sh" script is necessary to streamline the installation process and ensure that all required components are properly set up.
- Explain in at least 3-4 sentences how deploying KASM is related to/requires other topics talked about in the lesson and/or potential ways to add things mentioned in the lesson to this guide.
- Deploying KASM involves various related topics and potential additions from the lesson, including:
- Networking: Configuring network settings for KASM to ensure proper communication between the deployed application and other systems.
- Security: Implementing appropriate security measures, such as setting up firewalls or using encryption protocols, to protect the deployed KASM instance.
- System administration: Managing and monitoring the KASM deployment, performing updates, and troubleshooting issues.
- Integration: Integrating KASM with other tools, frameworks, or services mentioned in the lesson, such as Docker containers, load balancers, or monitoring solutions, to enhance functionality and performance. Total: 0.2 points
See the setup post