9.1 What is inheritance?
- Inheritance is like a family, except the kids only have one parent instead of two
- For example:
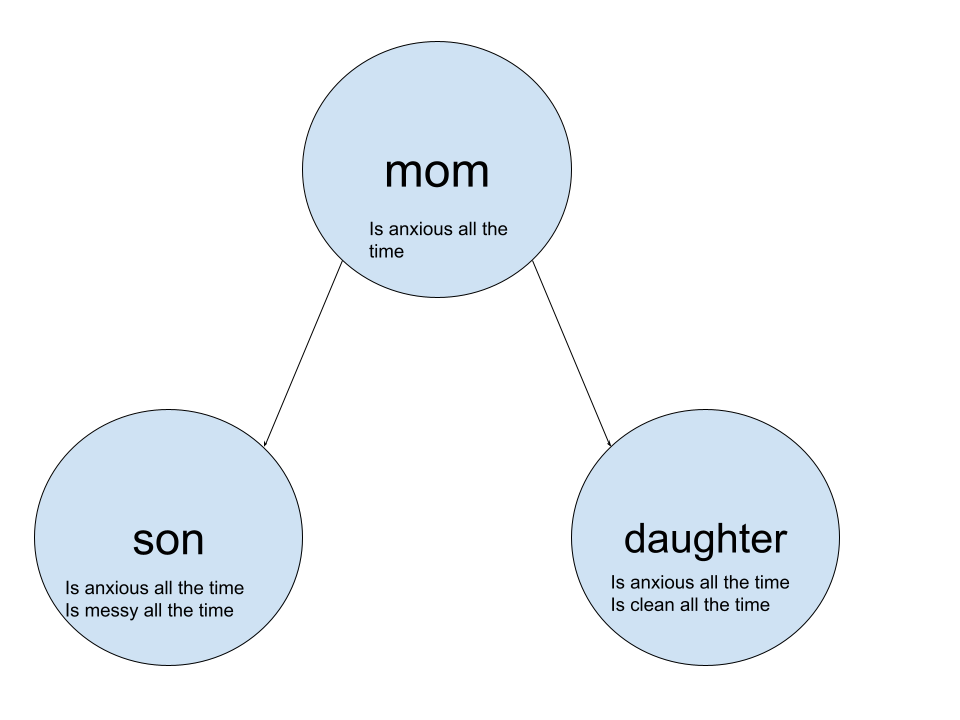
The java code for it:
class Mom{
// CODE
}
class Son extends Mom{
// CODE
}
class Daughter extends Mom{
// CODE
}
In this example, the Son and Daughter inherits the Mom, meaning it inherit the components of the mother. This makes the “Son” and “Daughter” classes the __ subclass__ of the “Mom” class as they inherit the “Mom” class components and the “Mom” class the superclass_.
9.2 Using the Super keyword for Constructors
- One keyword to know is the super keyword
- The super keyword allows the subclass to store key variables in the main class’s _ instance variables___ (also known as the super class)
- Example below:
%maven org.knowm.xchart:xchart:3.5.2
import org.knowm.xchart.*;
public class CardioidGraph {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int numPoints = 360; // Increase for a smoother cardioid
double[] xData = new double[numPoints];
double[] yData = new double[numPoints];
plotCardioid(xData, yData, 0, 0, numPoints - 1);
// Create Chart
XYChart chart = new XYChartBuilder().width(800).height(600).title("Cardioid Shape").xAxisTitle("X").yAxisTitle("Y").build();
chart.addSeries("Cardioid Shape", xData, yData);
// Show it
new SwingWrapper(chart).displayChart();
}
private static void plotCardioid(double[] xData, double[] yData, int index, double t, int maxIndex) {
if (index > maxIndex) {
return;
}
double r = 50; // Adjust the radius as needed
double a = 1; // Adjust the "a" value for the cardioid shape
double x = r * (a - Math.cos(t)) * Math.cos(t);
double y = r * (a - Math.cos(t)) * Math.sin(t);
xData[index] = x;
yData[index] = y;
plotCardioid(xData, yData, index + 1, t + (2 * Math.PI) / maxIndex, maxIndex);
}
}
CardioidGraph.main(null)
The Kernel crashed while executing code in the the current cell or a previous cell. Please review the code in the cell(s) to identify a possible cause of the failure. Click <a href='https://aka.ms/vscodeJupyterKernelCrash'>here</a> for more info. View Jupyter <a href='command:jupyter.viewOutput'>log</a> for further details.
Popcorn Hack:
Make it so that a new instance of Bob runs message any of us on slack “I” for an extra 0.01 (max of 1/1) <—– HMMMMMMM
public class Worker{
String Name;
int Age;
double Salary;
public Worker(String name, int age, double salary){
//Write codes that inherits its key properties
this.Name = name;
this.Age = age;
this.Salary = salary;
}
}
public class Bob extends Worker{
String Position;
public Bob(String name, int age, double salary,String position){
super(name, age, salary);
this.Position = position;
//Write code that maintains bob's information
}
public void Information(){
//Write code that writes out Bob's key information
System.out.println("Name: " + super.Name);
System.out.println("Age: " + super.Age);
System.out.println("Salary: " + super.Salary);
System.out.println("Position: " + this.Position);
}
}
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
//Make sure that it runs
Bob bob = new Bob("Bob", 20, 100000, "Manager");
bob.Information();
}
}
Test.main(null);
Name: Bob
Age: 20
Salary: 100000.0
Position: Manager
9.3 Overriding Methods
Method overriding is a concept in object-oriented programming (OOP) that allows a subclass to provide a specific implementation of a method that is already defined in its superclass. This enables a subclass to provide its own behavior for a method while maintaining a relationship with its superclass.
In the context Java, here’s how method overriding works:
Inheritance: Method overriding is closely related to inheritance. You have a superclass (or base class) and a subclass (or derived class). The subclass inherits properties and behaviors from the superclass.
Superclass Method: The superclass defines a method. This method can be overridden by the subclass.
Subclass Overrides: In the subclass, you can provide a new implementation of the same method. This is done by using the same method name, return type, and parameter list.
@Override Annotation (Java): In Java, it’s common to use the @Override annotation to explicitly indicate that a method in the subclass is intended to override a method in the superclass. This helps catch errors during compilation if the method doesn’t correctly match the superclass method signature.
message any of us on slack “Love” for an extra 0.01 (max of 1/1) <— HMMMMM
Why Override Methods:
Method overriding is used for several reasons:
Customization: It allows you to customize or extend the behavior of a superclass method in the subclass to meet the specific needs of the subclass.
Polymorphism: Method overriding is a key component of polymorphism. It enables you to treat objects of the subclass as if they were objects of the superclass, promoting flexibility and extensibility.
Consistency: Method overriding helps maintain a consistent interface for classes in an inheritance hierarchy. Code that uses the superclass doesn’t need to be changed when a subclass overrides a method.
Code Reusability: It promotes code reusability by allowing you to build on existing code in the superclass.
class Animal {
void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Animals make sounds");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
@Override
void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Dog barks");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal {
@Override
void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Cat meows");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal animal = new Animal();
Animal dog = new Dog();
Animal cat = new Cat();
animal.makeSound(); // Output: Animals make sounds
dog.makeSound(); // Output: Dog barks
cat.makeSound(); // Output: Cat meows
}
}
Main.main(null);
Animals make sounds
Dog barks
Cat meows
In this example:
We have a base class Animal with a method makeSound().
We create two subclasses, Dog and Cat, which inherit from the Animal class.
Both Dog and Cat classes override the makeSound() method with their own implementations.
In the main method, we create instances of the base class and its subclasses.
We demonstrate polymorphism by calling the makeSound() method on objects of the base class and the subclasses. The method called depends on the actual type of the object, not the reference type.
This showcases how method overriding allows you to provide specific implementations for methods in subclasses, promoting polymorphism and custom behavior for each subclass.
Another Example:
<img class=”image” src=”https://github.com/AniCricKet/musical-guacamole/assets/91163802/576237f9-cdc4-409b-84f9-96dffe0cdd5c” width=32%> <img class=”image” src=”https://github.com/AniCricKet/musical-guacamole/assets/91163802/03923e22-2b6e-4e4d-9244-1d5145f6c6d9” width=32%> <img class=”image” src=”https://github.com/AniCricKet/musical-guacamole/assets/91163802/5fe0c72c-c17b-4edb-a567-8c9098998aac” width=32%>
Imagine you’re building a program to manage sports team rosters. You can have a base class ‘Athlete’ representing common attributes and actions of all athletes. Then, create subclasses for specific sports like ‘FootballPlayer’, ‘BasketballPlayer’, and ‘SoccerPlayer’.
// Base Class
class Athlete {
String name;
int age;
int jerseyNumber;
String position;
public Athlete(String name, int age, int jerseyNumber, String position) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.jerseyNumber = jerseyNumber;
this.position = position;
}
public void train() {
System.out.println(name + " is training.");
}
public void displayInfo() {
System.out.println("Athlete Info:");
System.out.println("Name: " + name);
System.out.println("Age: " + age);
System.out.println("Jersey Number: " + jerseyNumber);
System.out.println("Position: " + position);
}
}
Athlete athlete = new Athlete("John Mortensen", 19, 4, "Teacher");
athlete.train();
athlete.displayInfo();
John Mortensen is training.
Athlete Info:
Name: John Mortensen
Age: 19
Jersey Number: 4
Position: Teacher
class FootballPlayer extends Athlete {
public FootballPlayer(String name, int age, int jerseyNumber, String position) {
super(name, age, jerseyNumber, position);
}
@Override
public void train() {
System.out.println(name + " is practicing football drills.");
}
@Override
public void displayInfo() {
super.displayInfo();
}
}
class BasketballPlayer extends Athlete {
public BasketballPlayer(String name, int age, int jerseyNumber, String position) {
super(name, age, jerseyNumber, position);
}
@Override
public void train() {
System.out.println(name + " is shooting 3s on the court.");
}
@Override
public void displayInfo() {
super.displayInfo();
}
}
class SoccerPlayer extends Athlete {
public SoccerPlayer(String name, int age, int jerseyNumber, String position) {
super(name, age, jerseyNumber, position);
}
@Override
public void train() {
System.out.println(name + " is practicing taking free kicks.");
}
@Override
public void displayInfo() {
super.displayInfo();
}
}
FootballPlayer footballPlayer = new FootballPlayer("Tyreek Hill", 28, 10, "Wide Receiver");
BasketballPlayer basketballPlayer = new BasketballPlayer("Jimmy Butler", 32, 22, "Small Forward");
SoccerPlayer soccerPlayer = new SoccerPlayer("Neymar Jr", 31, 10, "Left Winger");
footballPlayer.train();
footballPlayer.displayInfo();
System.out.println();
basketballPlayer.train();
basketballPlayer.displayInfo();
System.out.println();
soccerPlayer.train();
soccerPlayer.displayInfo();
System.out.println();
Tyreek Hill is practicing football drills.
Athlete Info:
Name: Tyreek Hill
Age: 28
Jersey Number: 10
Position: Wide Receiver
Jimmy Butler is shooting 3s on the court.
Athlete Info:
Name: Jimmy Butler
Age: 32
Jersey Number: 22
Position: Small Forward
Neymar Jr is practicing taking free kicks.
Athlete Info:
Name: Neymar Jr
Age: 31
Jersey Number: 10
Position: Left Winger
Explanation:
In this Java code, you have a basic “Athlete” class with information and actions that all athletes share. Then, there are specific types of athletes (football, basketball, and soccer players) that inherit these common traits but also have their unique behaviors, like training routines. Method overriding lets them have their own way of training while keeping the shared information, making the code easy to manage and reuse for different types of athletes.
Popcorn Hack:
Why is it helpful to have a common base class like ‘Athlete’ for all these different types of athletes? How does it make the code more organized?
ANS: with a base class Athelete, we are able to have a common set of methods that can be used by all athletes. This makes it easier to manage and reuse the code. Then, we can use override to change specific details of different Athletes we make. Lastly, it gives us multiple subclasses for different types of athletes and in this case, something they might do.
9.4 Using Super keyword for Methods
- Why only use super for constructors when you can use them for methods too?
- With the super key word, not only can you store variables, but also store methods
class Animal{
public void Introduction(String name){
System.out.println("I am a " + name);
}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
public void Woof(){
super.Introduction("Dog");//Inherits the introduction method in the Animal Class, then introduces itself as a dog
System.out.println("Woof!"); //Does its own thing
}
}
class Cow extends Animal{
public void Moo(){
super.Introduction("Cow");//Inherits the introduction method in the Animal Class, then introduces itself as a cow
System.out.println("MOOOO!");//Does its own thing
}
}
class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
Dog dog = new Dog();
Cow cow = new Cow();
dog.Woof();
cow.Moo();
}
}
Test.main(null);
I am a Dog
Woof!
I am a Cow
MOOOO!
9.4 Hack
Finish up the code with this criteria: All subclasses must say their origin, the origin can be from SchoolSupply class, and it must run through main.
class SchoolSupply {
// Declare instance variables for Pencil and Eraser
int Pencil = 100;
int Eraser = 50;
public void BasicInfo() {
// Output the basic information
System.out.println("This is a School Supply.");
System.out.println("Pencils: " + Pencil);
System.out.println("Erasers: " + Eraser);
}
}
class Pencil extends SchoolSupply {
public void Information() {
// Output Pencil-specific information
System.out.println("This is a Pencil.");
System.out.println("Origin: SchoolSupply");
}
}
class Eraser extends SchoolSupply {
public void Information() {
// Output Eraser-specific information
System.out.println("This is an Eraser.");
System.out.println("Origin: SchoolSupply");
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Pencil pencil = new Pencil();
Eraser eraser = new Eraser();
// Output basic information for Pencil and Eraser
pencil.BasicInfo();
eraser.BasicInfo();
// Output specific information for Pencil and Eraser
pencil.Information();
eraser.Information();
}
}
Test.main(null);
This is a School Supply.
Pencils: 100
Erasers: 50
This is a School Supply.
Pencils: 100
Erasers: 50
This is a Pencil.
Origin: SchoolSupply
This is an Eraser.
Origin: SchoolSupply
9.5 Creating References Using Inheritance Hierarchies
Inheritance can be thought as an upside down tree with the roots __ on the top and the _ branches_ on the bottom. The __ roots __ is the superclass while the __ branches__ are the subclasses of this superclass. A visual representation of this tree is called a type diagram or hierarchy tree.
A sample structure would be like:
public class A
public class B extends A
public class C extends B
public class D extends C
public class E extends I
public class F extends I
public class G extends H
public class H extends A
public class I extends H
Popcorn Hack
- Draw a hierarchy tree for the above structure and add the picture here
This structure works as C not only inherits properties from B, but it also inherits properties from A. B is like C’s parent and A is like C’s grandparent. Think about it like real life, all families inherit something from their ancestors.
In addition, you could also create objects like this:
C c = new C();
B c = new C();
A c = new C();

// This is the above example in code form
class A {}
class B extends A {}
class C extends B {}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
C c = new C(); // variable c is of type C
B b = new C(); // variable b is of type B, but refers to an instance of C
A a = new C(); // variable a is of type A, but refers to an instance of C
}
}
9.6 Polymorphism
A ____reference_ variable is polymorphic when it can refer to objects from different classes at different points in time
- A reference variable can store a reference to its declared class or any subclass of it’s declared class
A method or operator are considered polymorphic when they are __overridden__ in at least one subclass
Polymorphism is the act of executing an overridden non-__static___ method from the correct class at runtime based on the actual object type
Polymorphism allows __code __ for a method call to be executed based on the class of the object referenced instead of the declared class
Example 1
Java polymorphism is mainly split into 2 types
Runtime_____
- Process in which a function call to the overridden method is resolved at Runtime. This type of polymorphism is achieved by Method Overriding.
Compile polymorphism_____
- Also known as static polymorphism. This type is achieved by function overloading or operater overloading
- Note: But java doesnt support Operator Overloading
- When there are multiple functions with the same name but different parameters then these functions are said to be overloaded. Functions can be overloaded by changes in the number of arguments or/and a change in the type of arguments.
Here is an example of compile polymorphism
// Class 1
// Helper class
class Helper {
// Method 1
// Multiplication of 2 numbers
static int Multiply(int a, int b)
{
// Return product
return a * b;
}
// Method 2
// // Multiplication of 3 numbers
static int Multiply(int a, int b, int c)
{
// Return product
return a * b * c;
}
}
// Class 2
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Calling method by passing
// input as in arguments
System.out.println(Helper.Multiply(2, 4));
System.out.println(Helper.Multiply(2, 7, 3));
}
}
GFG.main(null)
8
42
Example 2 & Popcorn Hack
Before executing cell, look at the example below. Think about which methods compiles? Which methods execute?
message any of us on slack “Inheritance” for an extra 0.01 (max of 1/1) <—hmmmmm
import java.util.Random;
public class Entertainer{
private String talent;
public Entertainer (String t){
talent = t;
}
public String getTalent(){
return talent;
}
}
public class Comedian extends Entertainer{
private ArrayList<String> jokes;
public Comedian(String t, ArrayList<String> jks){
super(t);
jokes = jks;
}
public String getTalent(){
return "Comedy style: " + super.getTalent();
}
public String tellJoke(){
return jokes.get((int)(Math.random()*jokes.size()));
}
}
// Which one of these will run? Which one of these will not? Comment out the line that isn't working and explain why
Entertainer kevin = new Entertainer("Musician");
System.out.println(kevin.getTalent());
//System.out.println(kevin.tellJoke()); This will not run because tellJoke is not a method of Entertainer
ArrayList<String> oneLiners = new ArrayList<String>();
oneLiners.add("test"); //bruh
//Add code which adds jokes to oneLiners like... Why did the programmer quit his job?.. Why did the developer go broke?..
Entertainer soham = new Comedian(“satire”, oneliners);
System.out.println(soham.getTalent());
Musician
| Entertainer soham = new Comedian(“satire”, oneliners);
illegal character: '\u201c'
Example 3
Here is an example of runtime polymorphism
// Class 1
// Helper class
class Parent {
// Method of parent class
void Print()
{
// Print statement
System.out.println("parent class");
}
}
// Class 2
// Helper class
class subclass1 extends Parent {
// Method
void Print() { System.out.println("subclass1"); }
}
// Class 3
// Helper class
class subclass2 extends Parent {
// Method
void Print()
{
// Print statement
System.out.println("subclass2");
}
}
// Class 4
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating object of class 1
Parent a;
// Now we will be calling print methods
// inside main() method
a = new subclass1();
a.Print();
a = new subclass2();
a.Print();
}
}
GFG.main(null)
subclass1
subclass2
9.7 Object Superclass
Now that we have learned about inheritance, what even allows our classes and objects that we have created to work the way they do? Where do the general characteristics of all objects come from? The answer lies in the __object __ class.
The _ object___ class is the superclass of all other classes as well as arrays and other data types. The Object class is part of the java.lang package.
When we call a constructor to a “top-level class” that the coder hasn’t declared a superclass for, the Object constructor is implicitly called. In other words, the Object constructor is implicitly called when we call a constructor in a class that doesn’t explicitly extend another class. This will give the object some properties and methods that are common to all classes.
Example 1
public class Person {
String name;
int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person person1 = new Person("Jane Doe", 30);
Person person2 = new Person("Jane Doe", 30);
System.out.println(person1.equals(person1)); // Since person1 and person1 are the same object, the equals() method will return true
System.out.println(person1.equals(person2)); // Since person1 and person2 are different objects, the equals() method will return false even though they have the same contents
}
}
Person.main(null);
// The equals() method is inherited from the Object class
// By default, the equals() method in the Object class checks for object identity, which means it compares memory addresses to see if two references point to the exact same object
// In the code, person1 and person2 are distinct objects, so they have different memory addresses
// When we call person1.equals(person2), it checks if the memory addresses are the same (which they are not), so it returns false.
true
false
Example 2
public class Book {
String title;
String author;
public Book(String title, String author) {
this.title = title;
this.author = author;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Book book = new Book("The Catcher in the Rye", "J.D. Salinger");
int hashCode = book.hashCode();
System.out.println("HashCode: " + hashCode); // The output will be a unique integer value representing the object's hash code. The integer value will be different every time you run it
}
}
Book.main(null);
// The hashCode() method in the Object class returns a unique integer value for each object
// This value is typically based on the object's memory address.
// In the code, when we call book.hashCode(), it generates a unique integer value representing the book object
// This value can be useful for various purposes, such as organizing objects in collections like HashMaps or HashSet where it helps in efficient retrieval of objects.
HashCode: 2094718255
Hacks
- Popcorn Hacks (0.2): Participate in the discussion and fill in all of the blanks.
- MC Questions (0.1): Answer the 10 MC questions below with short explanations
- FRQ Hacks (0.5): Make a complex FRQ that involves everything we taught. Be sure to have a sample solution along with scoring guidlines and how the solution is scored.
- Challenge (0.1): Make an example that uses everything we taught and it must run through main and uses input and output. Points will be awarded for complexity and creativity
MC Questions
the answer is the first one, since we are able to create a car with the vehicle reference as we print as Vehicle vehicle
C b = new B shouldn’t work because C is a superclass of B and thus shouldn’t be able to create a new B object as a result, it would work if B was a superclass of C.
3: The objects of class G should be able to be treated as objects for H and J because G is extended by H which is extended by J, and its thus in the hierarchy at the end of H and J, allowing it to be an object for H and J.
4: C-D-B is the heirarchy, meaning B must be a subclass of C if we follow the heirarchy.
5: it should be the compile error, as Bird is the parent of penguin, so we cannot just make a bird object as a result.
6: the 2nd one should be right as since J is a parent of K and L we can thus create objects from the 2 children.
7: Inheiritance because subclasses are only created by inheiriting from parents.
8: G-B-C-H, means that G is an indirect superclass of H.
9: the roots would be superclasses and the branches would be subclasses, as branches extend off of roots, and subclasses extend off of parents or the superclasses.
10: the object should be successfully assigned as subclasses inheirit the superclasses reference variables.
please let me know in grading if I got anything wrong and what I should know, cause theres not answer key. also you can use this as an opportunity to make it look like you put a lot of effort into grading, which you did if you do this.
- FRQ Hacks (0.5): Make a complex FRQ that involves everything we taught. Be sure to have a sample solution along with scoring guidlines and how the solution is scored.
FRQ: at the local bakery, you are to build a class that can store information about baked goods.
Write a Java program that defines two subclasses, Dog and Cat, both inheriting from the Animal class. The Dog class should have properties for name, age, and breed, and a method called bark. The Cat class should have properties for name, age, and whether it is hypoallergenic, and a method called purr. In the main method, create instances of both Dog and Cat, and call their respective methods to demonstrate their behavior.
public class Animal {
// Your code goes here
public static class Dog extends Animal {
// Create the Dog subclass here
private String breed;
public Dog(String name, int age, String breed) {
// Initialize Dog properties here
}
public void bark() {
// Implement the bark method here
}
}
public static class Cat extends Animal {
// Create the Cat subclass here
private boolean isHypoallergenic;
public Cat(String name, int age, boolean isHypoallergenic) {
// Initialize Cat properties here
}
public void purr() {
// Implement the purr method here
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create instances of Dog and Cat, call their methods
Dog myDog = new Dog("Buddy", 3, "Golden Retriever");
myDog.bark();
Cat myCat = new Cat("Whiskers", 4, true);
myCat.purr();
}
}
Answer
public class Animal {
private String name;
private int age;
public Animal(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
// Part A
//
//
//
public static class Dog extends Animal {
private String breed;
public Dog(String name, int age, String breed) {
super(name, age);
this.breed = breed;
}
public void bark() {
System.out.println(getName() + " the " + breed + " is barking!");
}
}
// Part B
//
//
//
public static class Cat extends Animal {
private boolean isHypoallergenic;
public Cat(String name, int age, boolean isHypoallergenic) {
super(name, age);
this.isHypoallergenic = isHypoallergenic;
}
public void purr() {
System.out.println(getName() + " is " + getAge() + " years old and is purring.");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog myDog = new Dog("Buddy", 3, "Golden Retriever");
myDog.bark();
Cat myCat = new Cat("Whiskers", 4, true);
myCat.purr();
}
}
Animal.main(null);
Buddy the Golden Retriever is barking!
Whiskers is 4 years old and is purring
scoring
- 1/1 for making a dog class
- 1/1 for making a cat class
- 1/1 for the code working
- 1/1 for the super code being used in the classes
- 1/1 for correctly calling the functions from the objects